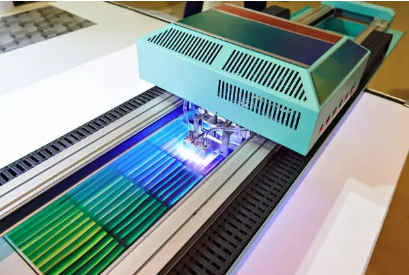
The Science Behind UV Curing: How It Works
Understanding the Chemistry: UV Light and Polymerization
When discussing UV curing, it is essential to delve into the chemical processes that lay the foundation for this technology. UV curing involves the use of ultraviolet light to initiate the polymerization process, transforming liquid resins into solid materials almost instantaneously. At its core, polymerization is a chemical reaction that links small molecules, known as monomers, into larger, more complex structures called polymers. This transformation occurs when UV photons are absorbed by certain substances, leading to the formation of free radicals or cations, depending on the type of photoinitiator used. These active species then engage with monomers present in the resin, facilitating the growth of a polymer network that hardens upon exposure to UV light. In practical applications, UV curing is not just a simple “turn on the light” affair. The energy wavelength of the UV light, typically ranging from 200 to 400 nm, plays a critical role in the effectiveness of the curing process. Different materials respond optimally to specific UV ranges, making it paramount to tailor the light source accordingly. Moreover, the efficiency of polymerization can also be influenced by dynamic factors such as temperature and resin viscosity, which can dictate how quickly the reaction proceeds and, ultimately, the physical characteristics of the cured resin. Importantly, this curing process results in an extremely durable and robust finish that can outperform traditional curing methods in terms of scratch resistance, chemical resistance, and thermal stability.
Key Components: From Resins to Photoinitiators
The performance of UV curing systems is heavily dependent on the quality of the components used, most notably the resins and photoinitiators. The resins, often formulated from acrylates or oligomers, determine the properties of the final cured product, such as flexibility, hardness, adhesion, and chemical resistance. These materials are specially designed to react under UV light, ensuring that they achieve the desired physical properties once cured. Photoinitiators are equally crucial to the UV curing process. These are compounds that absorb UV light and generate the free radicals or cations necessary for initiating polymerization. There are two primary types of photoinitiators: Type I, which generates free radicals upon exposure to UV light, and Type II, which produces cations. The choice between them can dramatically affect the curing speed and effectiveness. For instance, using a hybrid system that combines both types can yield superior results in applications requiring both rapid curing and excellent stability. Moreover, advancements in recent years have led to the development of specialized photoinitiators that perform effectively under lower energy UV wavelengths, making it possible to use LED technology for curing processes. This shift is significant, allowing for more energy-efficient systems and reducing the overall carbon footprint of the coating and printing industries. Consequently, choosing the right combination of resins and photoinitiators is imperative for optimizing UV curing performance and ensuring that the final outcome meets stringent quality requirements.
Benefits of UV Curing: Why It’s a Game Changer
Speed and Efficiency: The Rapid Cure Revolution
One of the foremost advantages of UV curing is its unmatched speed and efficiency. Unlike traditional drying methods that often involve prolonged exposure to heat or air, UV curing can achieve a fully cured finish in mere seconds. This drastic reduction in curing time translates directly into increased production capacity. Manufacturing lines can operate at higher speeds, ultimately leading to substantial cost savings. Businesses that adopt UV curing technology can handle higher volumes of work in shorter timeframes, granting them a competitive edge in fast-paced markets. Furthermore, UV curing technology is inherently more energy-efficient. Traditional solvent-based coatings require not only long drying times but also the use of heat, which can be detrimental to energy consumption and associated costs. UV curing eliminates the need for excessive energy expenditures by utilizing targeted UV light to efficiently cure coatings without significant energy losses. This efficiency is further underscored by the fact that UV systems generate less waste when compared to conventional systems, contributing to a more sustainable production process. The rapid curing phenomenon also reduces the chances of defects or imperfections during the drying process, minimizing the incidence of runs, sags, or dust contamination on freshly coated surfaces. In an age where quality control is paramount, these enhancements usher in a new standard of excellence where end products emerge continually polished and ready for immediate use or shipment.
Environmental Impact: Going Green with UV Technology
The environmental implications of UV curing cannot be overstated. One of the most significant benefits is its impact on reducing volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, which are prevalent in many traditional coating methods. VOCs are chemically reactive substances that can lead to air pollution, contributing to environmental degradation and posing health risks. UV-curable formulations typically contain little to no solvents, dramatically reducing the release of harmful substances into the atmosphere. Moreover, UV curing processes are designed to be more sustainable, as they often generate minimal waste. The photoinitiators and resins used can also be formulated to be more eco-friendly, leveraging renewable resources. As consumers and industries alike prioritize sustainability, the move toward UV curing aligns perfectly with corporate responsibility goals and regulatory standards established to curtail environmental harm. Additionally, the energy consumed during UV curing processes can be significantly lower than conventional drying methods, as these systems can often operate at lower temperatures and require less time, leading to reduced energy consumption overall. By embracing UV technology, businesses not only contribute positively to the environment but also position themselves advantageously in an increasingly eco-conscious market landscape.
Applications of UV Curing: Beyond Just Coatings
Innovations in Printing: Enhancing Durability and Vibrancy
While UV curing is often associated with coating applications, its footprint in the printing landscape is increasingly prominent. Traditional ink drying methods can result in issues such as smudging, fading, and poor adhesion on substrates. By employing UV-curable inks, businesses can achieve sharper, more vibrant prints that stand the test of time. These inks cure instantly upon exposure to UV light, leading to high-resolution images that are less susceptible to wear and tear. The versatility of UV printing systems is also worth noting. They can print on a multitude of substrates, from paper and cardboard to plastics and metals, thereby broadening the horizons for creative and innovative design possibilities. The ability to print on unconventional surfaces adds significant value to product packaging and promotional materials, allowing brands to differentiate themselves in a crowded marketplace. Moreover, UV technology contributes to enhancing the durability of printed materials. UV-cured prints exhibit superior resistance to scratches, chemicals, and UV exposure over time. This enhanced longevity is not only beneficial for marketing and aesthetic appeal but translates into cost-efficiency, as businesses can avoid frequent reprints, reducing wastage and resource expenditure.
Expanding Possibilities: UV Curing in Diverse Industries
The applications of UV curing extend far beyond coatings and printing, penetrating various sectors and offering solutions where traditional methods fall short. The automotive industry, for instance, has adopted UV curing for coatings and adhesives due to its speed and durability, crucial for maintaining quality in high-demand production environments. UV-curable adhesives are utilized in assembly processes, ensuring fast bonding times and robust performance, meeting the rigorous safety standards expected in vehicle production. Similarly, the electronics industry is leveraging UV curing in processes ranging from circuit board coatings to bonding components. Here, the precision of UV curing plays a critical role in achieving the high standards required in electronic products, where imperfections can lead to a compromise in functionality. The medical sector is not far behind, employing UV curing for medical device coatings and sterilization processes that require stringent quality controls. These coatings are crucial in ensuring that devices remain safe for patient use, consistently protecting against contamination and wear. In essence, the impregnations of UV technology across diverse industries signal a transformative era for production and processing workflows. Its ability to enhance efficiency, maintain quality, and minimize environmental impact makes UV curing a go-to choice for future-focused businesses seeking to innovate and thrive.
Choosing the Right UV Curing System: A Comprehensive Guide
Types of UV Systems: Comparing Options for Your Needs
As industries recognize the benefits of UV curing, selecting the right system becomes paramount to achieving optimal results. The market is rich with various UV curing technologies, each designed for specific applications. These systems can generally be classified into three primary categories: mercury vapor lamps, LED UV systems, and excimer lamps. Mercury vapor lamps have long been the traditional choice for industrial UV curing, offering a robust and high-intensity curing option. However, they require some time to heat up and produce UV light, thus not being the most energy-efficient solution available today. Conversely, LED UV systems have surged in popularity due to their instantaneous curing capabilities and lower energy consumption, allowing businesses to reduce overhead costs while also benefiting from longer lifetimes compared to mercury lamps. Excimer lamps are another advanced option that excels in specialized applications, particularly in the fields of photopolymerization and surface treatment. Their ability to emit energy at very specific wavelengths makes them suitable for curing materials that require precise treatments. Moreover, when selecting a UV system, one must factor in the workflow and production capabilities of your facility. Considerations such as the types of materials being cured, the required cure speed, and spatial limitations will significantly influence the choice of equipment.
Maintenance and Best Practices: Ensuring Optimal Performance
To maximize the lifespan and effectiveness of a UV curing system, regular maintenance and adherence to best practices are essential. One key aspect is monitoring lamp performance, as both mercury and LED lamps exhibit losses in intensity over time. Regularly replacing lamps as per manufacturer recommendations helps maintain consistent curing energy and quality across different runs. Additionally, keeping the curing chamber clean and free from dust and contaminants can prevent issues such as defects in the cured coating. Establishing a routine cleaning schedule will ensure that equipment remains in peak condition and minimizes downtime attributed to maintenance issues. Calibration of UV systems is another vital maintenance task that should not be overlooked. Ensuring that the UV intensity is correctly calibrated based on the materials being used is crucial for achieving optimal polymerization. In terms of best practices, conducting preliminary tests to establish curing parameters, such as exposure time and distance, can lead to better outcomes, ultimately resulting in higher quality products. Incorporating staff training into maintenance routines is equally important. Providing employees with proper education about the operation and upkeep of UV curing technology will empower them to identify potential issues early and maintain high operational standards. In conclusion, the world of UV curing is vast and offers transformative potential across various industries. By understanding the science behind the technology, the multitude of benefits it provides, and the extensive applications it encompasses, businesses can harness this powerful tool to enhance their production capabilities and create superior products. As UV curing continues to evolve, so too will the opportunities it presents, ensuring that this technology remains at the forefront of innovation in coatings, printing, and beyond.




